Resetting the 2004 Dodge Neon check engine light isn’t just about clearing a warning—it’s about understanding what triggered it in the first place. This guide walks you through safe reset methods, from using an OBD2 scanner to manual battery disconnection, while emphasizing the importance of diagnosing underlying issues to prevent recurring problems.
Key Takeaways
- Diagnose before resetting: Always use an OBD2 scanner to read trouble codes before clearing the check engine light to avoid masking serious engine problems.
- Use an OBD2 scanner for best results: This is the most reliable and recommended method to reset the light on a 2004 Dodge Neon.
- Battery disconnection is a temporary fix: While disconnecting the battery can reset the light, it may also erase important vehicle settings and doesn’t address root causes.
- Common triggers include O2 sensors and gas caps: Loose or faulty gas caps and oxygen sensors are frequent culprits behind the check engine light in this model.
- Monitor after reset: After clearing the light, drive the car for a few days to ensure the issue doesn’t return.
- Seek professional help if needed: If the light comes back repeatedly, consult a certified mechanic to avoid long-term damage.
- Regular maintenance prevents issues: Routine checks of spark plugs, air filters, and fuel systems can reduce the chances of future warning lights.
📑 Table of Contents
- Introduction: Understanding the 2004 Dodge Neon Check Engine Light
- Why the Check Engine Light Comes On in a 2004 Dodge Neon
- Tools You’ll Need to Reset the Check Engine Light
- Step-by-Step Guide: How to Reset the Check Engine Light
- What to Do After Resetting the Check Engine Light
- Preventing Future Check Engine Light Issues
- Conclusion: Take Control of Your Neon’s Health
Introduction: Understanding the 2004 Dodge Neon Check Engine Light
The check engine light in your 2004 Dodge Neon isn’t just a random annoyance—it’s your car’s way of saying, “Hey, something needs attention.” Whether it’s a flickering glow on your dashboard or a steady amber glow, this warning signal should never be ignored. While it might seem tempting to just “make it go away,” understanding what caused it in the first place is crucial for your vehicle’s health and your safety on the road.
The 2004 Dodge Neon, part of the popular compact sedan lineup, relies on an onboard diagnostic system (OBD2) to monitor engine performance, emissions, and various sensors. When something goes outside normal parameters—like a misfire, low fuel pressure, or a loose gas cap—the system triggers the check engine light. Resetting it without addressing the root cause is like turning off a smoke alarm while the kitchen is still on fire. It might look fixed, but the problem remains.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about resetting the 2004 Dodge Neon check engine light—safely, effectively, and responsibly. From diagnosing the issue to choosing the right reset method, we’ll cover practical steps, common causes, and expert tips to keep your Neon running smoothly. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or just want to understand what’s happening under the hood, this guide has you covered.
Why the Check Engine Light Comes On in a 2004 Dodge Neon
Before you think about resetting the check engine light, it’s essential to understand why it came on in the first place. The 2004 Dodge Neon uses a sophisticated OBD2 system that monitors over a dozen engine and emissions components. When a sensor detects an anomaly—such as a drop in fuel efficiency, irregular combustion, or a failed emissions test—the system logs a trouble code and illuminates the check engine light.
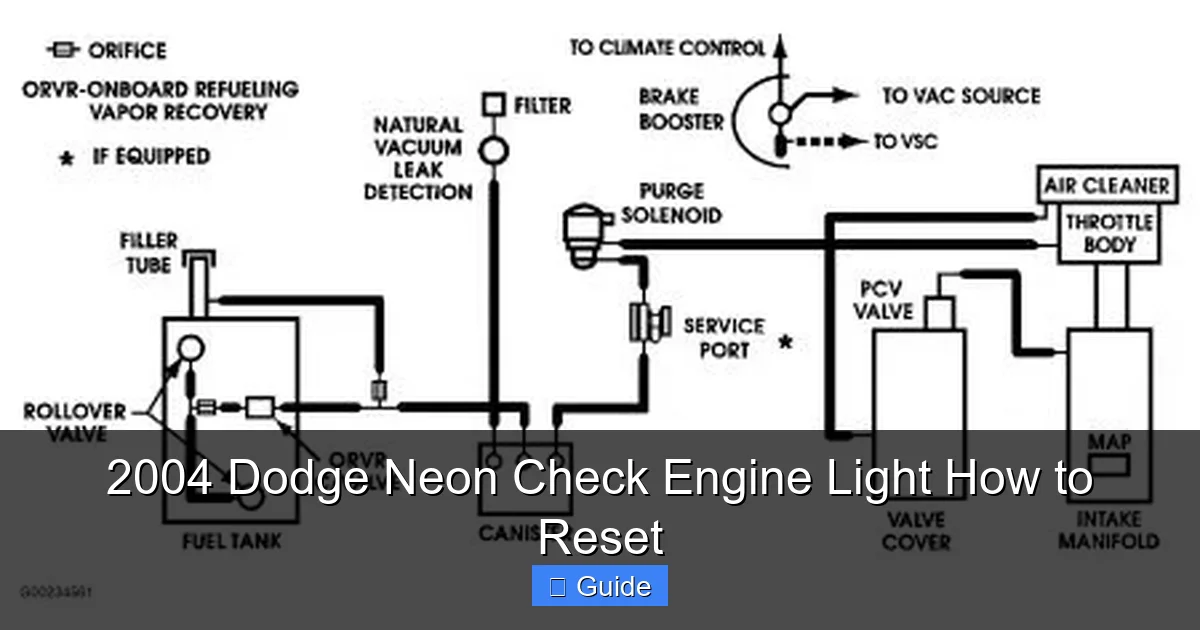
Visual guide about 2004 Dodge Neon Check Engine Light How to Reset
Image source: 2carpros.com
Common Causes of the Check Engine Light
Several issues frequently trigger the check engine light in the 2004 Dodge Neon. Some are minor and easy to fix, while others may require professional attention. Here are the most common culprits:
- Loose or Faulty Gas Cap: Believe it or not, a loose, cracked, or missing gas cap is one of the top reasons for the check engine light. It allows fuel vapors to escape, disrupting the evaporative emissions system. Simply tightening or replacing the cap often resolves the issue.
- Oxygen (O2) Sensor Failure: The O2 sensors monitor the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. A faulty sensor can lead to poor fuel economy, increased emissions, and engine performance issues. Replacing a bad O2 sensor is usually straightforward but may require a wrench and some patience.
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor Problems: The MAF sensor measures how much air enters the engine. If it’s dirty or malfunctioning, the engine may run rich or lean, causing hesitation, stalling, or poor acceleration. Cleaning it with MAF cleaner can sometimes fix the issue.
- Spark Plug or Ignition Coil Issues: Worn spark plugs or failing ignition coils can cause misfires, which trigger the check engine light. This is especially common in older Neons with high mileage. Replacing spark plugs every 30,000–60,000 miles is recommended.
- Catalytic Converter Failure: A clogged or damaged catalytic converter restricts exhaust flow and reduces performance. This is a more serious issue that often follows prolonged neglect of other problems like misfires or rich fuel mixtures.
- Evaporative Emissions (EVAP) System Leaks: The EVAP system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. Small leaks—often from cracked hoses or faulty purge valves—can trigger the light.
How the OBD2 System Works
The 2004 Dodge Neon is equipped with an OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) system, which became standard in all vehicles manufactured after 1996. This system continuously monitors engine performance and emissions through a network of sensors. When a problem is detected, the system stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in the vehicle’s computer and turns on the check engine light.
These codes follow a standard format, such as P0300 (random/multiple cylinder misfire) or P0420 (catalytic converter efficiency below threshold). By reading these codes with an OBD2 scanner, you can pinpoint the exact issue and take appropriate action. Ignoring the code and simply resetting the light without fixing the problem is risky—it could lead to decreased fuel efficiency, increased emissions, or even engine damage over time.
Tools You’ll Need to Reset the Check Engine Light
Resetting the check engine light on your 2004 Dodge Neon requires a few basic tools, depending on the method you choose. While some approaches are simple and require minimal equipment, others are more technical. Here’s what you’ll need for the most common reset methods:
OBD2 Scanner (Recommended)
An OBD2 scanner is the most reliable and professional way to reset the check engine light. These devices plug into the diagnostic port (usually under the dashboard near the steering column) and communicate directly with the car’s computer. Most modern scanners can read trouble codes, display live data, and clear the check engine light with the push of a button.
For the 2004 Dodge Neon, any standard OBD2 scanner will work—no special model is required. Affordable options like the BlueDriver, Innova 3100, or even basic Bluetooth scanners that pair with your smartphone are excellent choices. Some auto parts stores also offer free code reading services, though they may not allow you to clear the light yourself.
Basic Hand Tools (For Battery Disconnection)
If you’re using the battery disconnection method, you’ll need a few simple tools:
- A wrench or socket set (typically 10mm) to loosen the battery terminals
- Safety gloves and eye protection
- A clean cloth to wipe the terminals
Always disconnect the negative terminal first and reconnect it last to avoid electrical shorts. Be aware that disconnecting the battery may reset other systems, such as the radio presets, clock, and power window settings.
Optional: Multimeter (For Diagnostics)
While not required for a simple reset, a multimeter can help you test sensors, check battery voltage, or verify electrical connections. This is especially useful if you suspect a deeper electrical issue or want to confirm that a replaced part is working correctly.
Safety Gear
Always prioritize safety when working on your vehicle. Wear gloves to protect your hands from sharp edges or battery acid, and use eye protection when handling tools near the battery. Work in a well-ventilated area, and never smoke or use open flames near the fuel system.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Reset the Check Engine Light
Now that you understand the causes and have the right tools, let’s walk through the most effective ways to reset the check engine light on your 2004 Dodge Neon. We’ll cover three main methods: using an OBD2 scanner, disconnecting the battery, and driving the car to allow the system to reset naturally. Each has its pros and cons, so choose the one that best fits your situation.
Method 1: Using an OBD2 Scanner (Best Practice)
This is the most accurate and recommended method for resetting the check engine light. It allows you to read the trouble codes first, fix the underlying issue, and then clear the light confidently.
Step 1: Locate the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port in the 2004 Dodge Neon is typically located under the dashboard, to the left of the steering column. It’s a 16-pin connector, usually black or gray, and may be covered by a small panel. If you can’t find it, consult your owner’s manual or look for a diagram online.
Step 2: Plug in the Scanner
Turn off the ignition, then plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Make sure it’s securely connected. Some scanners require the ignition to be in the “ON” position (but engine off), while others work with the key out. Follow your scanner’s instructions.
Step 3: Read the Trouble Codes
Turn the ignition to the “ON” position (do not start the engine). The scanner should power up and display a menu. Select “Read Codes” or a similar option. The device will retrieve the stored DTCs and display them on the screen.
For example, you might see P0455 (large EVAP leak) or P0133 (O2 sensor slow response). Write down the codes and research their meanings using the scanner’s manual or an online database.
Step 4: Fix the Underlying Issue
Before clearing the light, address the problem. If the code points to a loose gas cap, tighten it. If it’s an O2 sensor, consider replacing it. Fixing the issue ensures the light won’t come back immediately.
Step 5: Clear the Codes
Once the issue is resolved, return to the scanner menu and select “Clear Codes” or “Erase DTCs.” The scanner will send a command to the car’s computer to reset the check engine light. The light should turn off within a few seconds.
Step 6: Verify the Reset
Start the engine and check the dashboard. The check engine light should remain off. If it comes back on, the problem may not be fully resolved, or a new issue may have developed.
Method 2: Disconnecting the Battery (Alternative Method)
If you don’t have an OBD2 scanner, disconnecting the battery can reset the check engine light. However, this method is less precise and may not work for all issues. It also resets other vehicle systems, so use it with caution.
Step 1: Turn Off the Engine and Remove the Key
Make sure the car is completely off and the key is out of the ignition. This prevents electrical surges or accidental starts.
Step 2: Locate the Battery
Open the hood and find the battery. In the 2004 Dodge Neon, it’s usually on the driver’s side, near the front of the engine bay.
Step 3: Disconnect the Negative Terminal
Use a wrench to loosen the nut on the negative (black) battery terminal. Carefully remove the cable and tuck it away from the battery post to prevent accidental contact.
Step 4: Wait 15–30 Minutes
Leave the battery disconnected for at least 15 minutes. This allows the car’s computer (ECU) to fully power down and reset its memory. Some recommend waiting up to 30 minutes for a complete reset.
Step 5: Reconnect the Battery
Reattach the negative terminal and tighten the nut securely. Make sure the connection is snug to avoid electrical issues.
Step 6: Start the Engine
Turn the key and start the car. The check engine light may flash briefly, then turn off. If it remains off, the reset was successful. If it comes back on, the underlying issue still exists.
Note: Disconnecting the battery may reset the radio, clock, and power windows. You may need to reprogram these features afterward.
Method 3: Drive Cycle Reset (Natural Method)
In some cases, the check engine light will turn off on its own after the problem is fixed and the car completes a “drive cycle.” A drive cycle is a series of driving conditions that allow the OBD2 system to retest the repaired components.
For the 2004 Dodge Neon, a typical drive cycle includes:
- Starting the engine when cold and letting it idle for 2–3 minutes
- Driving at a steady speed of 30–40 mph for 5–10 minutes
- Accelerating to 55–60 mph and maintaining that speed for several minutes
- Decelerating without braking (coasting)
- Repeating the cycle 2–3 times
After completing the drive cycle, the ECU will recheck the systems. If no faults are detected, the check engine light may turn off automatically. This method is passive but effective for minor issues like a recently tightened gas cap.
What to Do After Resetting the Check Engine Light
Resetting the check engine light is only the first step. To ensure your 2004 Dodge Neon stays in good condition, follow these post-reset best practices:
Monitor the Light
After clearing the light, drive your car normally for a few days. If the light stays off, the issue was likely resolved. If it returns, the problem persists and needs further attention. A recurring light often indicates a deeper mechanical or electrical issue.
Check for Pending Codes
Some OBD2 scanners can read “pending” codes—trouble codes that haven’t yet triggered the light but are being monitored. These can give you early warning of developing problems. Use your scanner to check for pending codes a few days after the reset.
Perform Routine Maintenance
Prevent future check engine light issues with regular maintenance. Replace spark plugs and wires every 30,000–60,000 miles, change the air filter every 15,000 miles, and inspect the fuel system annually. Keeping your Neon well-maintained reduces the risk of sensor failures and emissions problems.
Keep a Maintenance Log
Record when you reset the check engine light, what codes were present, and what repairs were made. This log helps track recurring issues and provides valuable information if you ever sell the car or take it to a mechanic.
Consult a Mechanic if Needed
If the light comes back repeatedly or you’re unsure about the cause, don’t hesitate to visit a certified mechanic. They have advanced diagnostic tools and can perform a thorough inspection. Ignoring persistent issues can lead to costly repairs down the road.
Preventing Future Check Engine Light Issues
The best way to deal with the check engine light is to prevent it from coming on in the first place. While some issues are unavoidable, many can be avoided with proactive care and attention.
Regular Inspections
Schedule regular inspections of key components, especially if your Neon has high mileage. Check the condition of the gas cap, hoses, belts, and sensors. Look for cracks, leaks, or wear and replace parts as needed.
Use Quality Fuel and Additives
Fill up at reputable gas stations and consider using a fuel system cleaner every 3,000–5,000 miles. This helps keep injectors clean and prevents carbon buildup, which can affect sensor readings.
Avoid Short Trips
Frequent short trips prevent the engine from reaching optimal operating temperature, which can lead to moisture buildup and sensor corrosion. When possible, combine errands into longer drives to help the engine run efficiently.
Listen to Your Car
Pay attention to changes in performance—hesitation, rough idling, or decreased fuel economy. These symptoms often precede a check engine light and can help you catch problems early.
Stay Informed
Join online forums or owner groups for 2004 Dodge Neon enthusiasts. These communities share tips, common issues, and solutions that can help you stay ahead of potential problems.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Neon’s Health
Resetting the 2004 Dodge Neon check engine light doesn’t have to be a mystery or a source of stress. With the right tools, knowledge, and approach, you can safely clear the light and keep your car running smoothly. Remember, the light is there to protect you—not to scare you. By diagnosing the issue first, choosing the best reset method, and following up with proper maintenance, you’ll extend the life of your Neon and avoid costly repairs.
Whether you use an OBD2 scanner, disconnect the battery, or let the system reset naturally, always prioritize safety and accuracy. And if you’re ever in doubt, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Your car deserves the best care, and so do you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I reset the check engine light without a scanner?
Yes, you can disconnect the battery to reset the light, but this method is less reliable and may not work for all issues. It also resets other vehicle settings like the radio and clock.
Will the check engine light reset itself?
In some cases, yes. If the problem is fixed and the car completes a proper drive cycle, the light may turn off automatically after the system retests the components.
How long does it take for the check engine light to reset after disconnecting the battery?
You should wait at least 15–30 minutes after disconnecting the battery to allow the ECU to fully reset. Reconnect the battery and start the engine to see if the light is off.
Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
It depends on the issue. A flashing light indicates a serious problem like a misfire, which can damage the catalytic converter. A steady light may be less urgent, but you should still diagnose it soon.
Why does my check engine light keep coming back after reset?
If the light returns, the underlying issue hasn’t been fixed. Common causes include faulty sensors, emissions leaks, or ongoing mechanical problems. Use an OBD2 scanner to read the codes and address the root cause.
Can a loose gas cap really trigger the check engine light?
Yes, absolutely. A loose, damaged, or missing gas cap allows fuel vapors to escape, triggering an EVAP system leak code. Tightening or replacing the cap often resolves the issue immediately.
