This guide walks you through how to reset the check engine light on a Polaris Ranger using simple methods like OBD2 scanners, battery disconnects, and built-in diagnostic modes. Always diagnose the root cause first to avoid recurring issues.
Key Takeaways
- Diagnose First: Never reset the check engine light without identifying and fixing the underlying problem—otherwise, it will return.
- Use an OBD2 Scanner: The most reliable method for reading codes and resetting the light on modern Polaris Rangers (2013 and newer).
- Battery Disconnect Works (Sometimes): Disconnecting the battery for 10–15 minutes can reset the ECU, but may not clear all trouble codes.
- Check Fuses and Connections: Loose or blown fuses can trigger false engine lights—inspect them before resetting.
- Reset via Diagnostic Mode (Older Models): Some older Rangers allow a manual reset using the instrument cluster buttons.
- Monitor After Reset: Drive the vehicle for a few cycles to ensure the light doesn’t return and the issue is truly resolved.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: If the light persists, consult a Polaris-certified technician to avoid engine damage.
How to Reset Check Engine Light Polaris Ranger
If you’re driving your Polaris Ranger and suddenly see that dreaded check engine light glowing on the dashboard, don’t panic—but don’t ignore it either. That little orange or yellow light is your vehicle’s way of saying, “Hey, something’s not right under the hood.” While it might be tempting to just make it go away, the real goal isn’t just to reset the check engine light on your Polaris Ranger—it’s to fix the problem causing it in the first place.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn everything you need to know about how to reset the check engine light on a Polaris Ranger safely and effectively. We’ll walk you through multiple methods—from using an OBD2 scanner to disconnecting the battery—and explain when each is appropriate. You’ll also learn how to interpret trouble codes, troubleshoot common issues, and avoid making the problem worse. Whether you’re a weekend trail rider or use your Ranger for work, this guide will help you keep your UTV running smoothly.
By the end of this article, you’ll be able to confidently diagnose, address, and reset that check engine light—so you can get back to what matters: enjoying your ride.
Understanding the Check Engine Light on a Polaris Ranger
Before you reset the check engine light, it’s important to understand what it actually means. The check engine light—also known as the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL)—is part of your Polaris Ranger’s onboard diagnostic system (OBD). When the engine control unit (ECU) detects a problem with the engine, emissions system, or related components, it stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and illuminates the light.
This light can come on for a wide range of reasons, from something as simple as a loose gas cap to more serious issues like a failing oxygen sensor or ignition coil problem. That’s why resetting the light without fixing the root cause is like turning off a smoke alarm while your kitchen is still on fire—it doesn’t solve the problem.
Modern Polaris Rangers (typically 2013 and newer) are equipped with OBD2 systems, which means they generate standardized trouble codes that can be read with a scanner. Older models may use proprietary systems, making diagnosis a bit trickier. But regardless of your model year, the first step should always be to determine why the light came on.
Why You Shouldn’t Just Reset the Light Immediately
It’s tempting to want that light gone as quickly as possible. But resetting the check engine light without addressing the underlying issue can lead to bigger problems down the road. For example, if the light is on because of a faulty oxygen sensor, continuing to drive without fixing it can reduce fuel efficiency, increase emissions, and even damage the catalytic converter over time.
Additionally, some issues—like misfires or low compression—can cause engine damage if ignored. The check engine light is your Ranger’s early warning system. Treat it with respect.
So, before you reset the light, ask yourself:
– Did I recently refuel? (A loose gas cap can trigger the light.)
– Have I noticed any performance issues, like rough idling or loss of power?
– Has the vehicle been exposed to water, mud, or extreme conditions?
Taking a few minutes to investigate can save you hundreds—or even thousands—in repair costs.
Method 1: Using an OBD2 Scanner (Recommended)
The most reliable and accurate way to reset the check engine light on a Polaris Ranger is by using an OBD2 scanner. This method allows you to read the trouble codes, understand what’s wrong, and then clear the codes once the issue is fixed.
What You’ll Need
- OBD2 scanner (Bluetooth or wired)
- Compatible smartphone app (if using a Bluetooth scanner)
- Access to the OBD2 port (usually under the dashboard)
Step-by-Step Instructions
Step 1: Locate the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port on most Polaris Rangers is located under the dashboard, near the driver’s side footwell. It’s a 16-pin connector, usually black or gray, and may be covered by a small plastic panel. If you can’t find it, consult your owner’s manual—Polaris sometimes places it behind the glove box or under the seat on certain models.
Visual guide about How to Reset Check Engine Light Polaris Ranger
Image source: i.pinimg.com
Step 2: Plug in the Scanner
Turn off the ignition, then plug the OBD2 scanner into the port. Make sure it’s fully seated. If you’re using a Bluetooth scanner, pair it with your smartphone and open the corresponding app (like Torque Pro or OBD Fusion).
Step 3: Turn the Ignition On (Do Not Start the Engine)
Turn the key to the “ON” position. The dashboard lights should illuminate, but the engine should remain off. This powers up the ECU and allows the scanner to communicate with the vehicle.
Step 4: Read the Trouble Codes
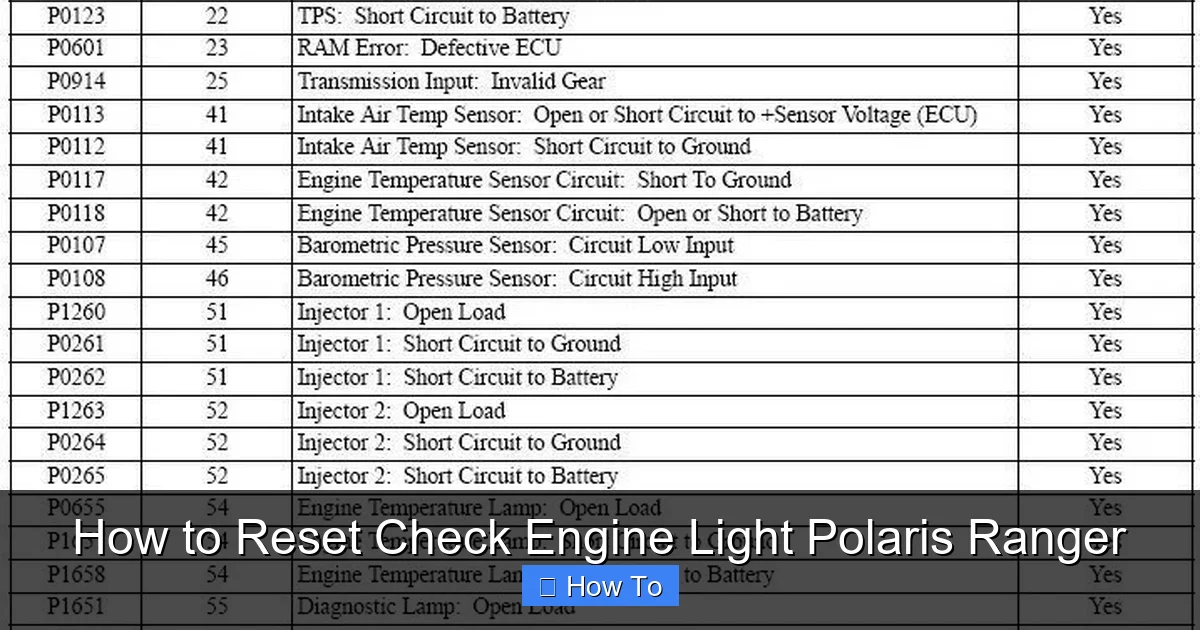
Follow the scanner’s prompts to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). The scanner will display codes like P0300 (random misfire) or P0420 (catalyst efficiency below threshold). Write these down—they’re crucial for diagnosing the problem.
Step 5: Research the Codes
Use the scanner’s built-in code definitions or search online for “Polaris Ranger [code] meaning.” For example, a P0171 code typically indicates a lean fuel mixture, which could be caused by a vacuum leak or faulty fuel injector.
Step 6: Fix the Underlying Issue
Once you’ve identified the problem, take steps to fix it. This might involve replacing a sensor, tightening a gas cap, or cleaning a throttle body. Never skip this step—resetting the light without a repair is pointless.
Step 7: Clear the Codes
After the repair, return to the scanner and select the option to “Clear Codes” or “Reset ECU.” The scanner will send a command to the ECU to erase the stored trouble codes and turn off the check engine light.
Step 8: Verify the Reset
Turn the ignition off, wait 10 seconds, then turn it back on. The check engine light should remain off. If it comes back on immediately, the problem may not be fully resolved, or a new issue has been detected.
Tips for Using an OBD2 Scanner
- Choose a scanner that supports Polaris-specific codes if possible. Generic OBD2 scanners may not read all manufacturer-specific data.
- Keep the scanner updated with the latest software to ensure compatibility.
- If the light returns after a few drive cycles, the issue may be intermittent or require professional diagnosis.
Method 2: Disconnecting the Battery
If you don’t have an OBD2 scanner, disconnecting the battery is a common alternative method to reset the check engine light. This process forces the ECU to reset by cutting power, which clears temporary memory and stored trouble codes.
How It Works
When you disconnect the battery, the ECU loses power and resets to its default settings. This can clear the check engine light—but only if the underlying issue has been resolved. If the problem still exists, the light will likely return after a few drive cycles.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Step 1: Turn Off the Ignition
Make sure the key is in the “OFF” position and remove it from the ignition.
Step 2: Locate the Battery
On most Polaris Rangers, the battery is located under the passenger seat or in the front storage compartment. Lift the seat or open the compartment to access it.
Step 3: Disconnect the Negative Terminal
Use a wrench or socket to loosen the nut on the negative (black) battery terminal. Carefully remove the cable and set it aside, making sure it doesn’t touch the battery post.
Step 4: Wait 10–15 Minutes
This allows the ECU to fully discharge and reset. Some mechanics recommend waiting up to 30 minutes for a complete reset, especially on newer models with advanced electronics.
Step 5: Reconnect the Battery
Reattach the negative terminal and tighten the nut securely. Make sure the connection is clean and tight to avoid electrical issues.
Step 6: Turn the Ignition On
Turn the key to the “ON” position and check the dashboard. The check engine light should be off. Start the engine and let it idle for a few minutes to allow the ECU to relearn basic parameters.
Limitations of Battery Disconnect
- May not clear all trouble codes, especially on newer models with persistent memory.
- Can reset other systems, like radio presets, clock, and security settings.
- Does not diagnose the problem—only masks it temporarily.
Method 3: Using the Instrument Cluster (Older Models)
Some older Polaris Rangers (pre-2013) don’t have a standard OBD2 port or may use a proprietary diagnostic system. In these cases, you may be able to reset the check engine light using the instrument cluster buttons.
Step-by-Step Instructions
Step 1: Turn the Ignition On
Turn the key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
Step 2: Press and Hold the Mode Button
Locate the mode or trip button on the instrument cluster (usually near the speedometer). Press and hold it for 10–15 seconds.
Step 3: Watch for the Light to Flash
The check engine light may flash or turn off, indicating a reset. Some models require you to cycle through menu options using the button.
Step 4: Turn Off the Ignition
Release the button and turn the key to “OFF.” Wait 30 seconds, then turn it back on to verify the light is off.
Note
This method is not guaranteed to work on all older Rangers. Consult your owner’s manual or contact Polaris support for model-specific instructions.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even after resetting the light, it may come back. Here are some common reasons why and how to fix them.
Check Engine Light Returns Immediately
If the light comes back on right after startup, the problem hasn’t been fixed. Use an OBD2 scanner to read the new codes and address the issue. Common causes include faulty sensors, loose wiring, or ongoing engine misfires.
Light Returns After a Few Miles
This suggests an intermittent issue. For example, a loose gas cap might seal temporarily but leak after driving. Recheck all connections, seals, and recent repairs.
Battery Disconnect Didn’t Work
On newer Rangers, the ECU may retain codes even after a battery disconnect. Use an OBD2 scanner for a more reliable reset.
No OBD2 Port Found
Some early models don’t have a standard OBD2 port. In these cases, you may need a Polaris-specific diagnostic tool or professional assistance.
Preventing Future Check Engine Light Issues
The best way to avoid dealing with the check engine light is to prevent it from coming on in the first place. Here are some proactive maintenance tips:
- Regular Oil Changes: Use the recommended oil type and change it every 50–100 hours of operation.
- Check the Air Filter: Clean or replace it regularly, especially if you ride in dusty conditions.
- Inspect Spark Plugs: Replace them every 100–200 hours or as recommended.
- Tighten the Gas Cap: After refueling, make sure the cap is securely tightened.
- Use Quality Fuel: Avoid ethanol-blended fuels if possible, as they can cause sensor issues.
- Keep the Engine Clean: Wash your Ranger regularly to prevent dirt and debris from clogging sensors.
When to See a Mechanic
While many check engine light issues can be resolved at home, some problems require professional attention. Seek help if:
- The light is flashing (indicates a severe misfire that can damage the catalytic converter).
- You notice smoke, strange noises, or loss of power.
- The light returns repeatedly despite repairs.
- You’re unable to read or interpret the trouble codes.
A Polaris-certified technician has access to advanced diagnostic tools and can perform a thorough inspection.
Conclusion
Resetting the check engine light on your Polaris Ranger doesn’t have to be intimidating. Whether you use an OBD2 scanner, disconnect the battery, or use the instrument cluster, the key is to always diagnose and fix the problem first. Simply turning off the light without addressing the cause is a temporary fix that can lead to bigger issues.
By following the steps in this guide, you’ll not only learn how to reset the check engine light on a Polaris Ranger but also how to keep your UTV running at its best. Remember: the light is there to help you. Listen to it, respect it, and your Ranger will reward you with reliable performance for years to come.
