This guide walks you through how to disconnect the engine light on a 1996 Ford Ranger using simple tools and safe methods. You’ll learn why the light comes on, how to reset it properly, and when it’s best to consult a mechanic instead.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the cause first: The check engine light can signal minor issues like a loose gas cap or serious problems like engine misfires—always diagnose before resetting.
- Use an OBD-I scanner for accuracy: The 1996 Ford Ranger uses OBD-I, so a compatible scanner is the most reliable way to read and clear codes.
- Battery disconnection works temporarily: Pulling the negative battery cable for 10–15 minutes can reset the ECU and turn off the light, but it may return if the issue persists.
- Avoid cutting wires: Never physically disconnect the engine light bulb—it’s unsafe, illegal in some areas, and can damage your vehicle’s electrical system.
- Reset the PCM manually: Some models allow a manual PCM reset by turning the ignition on and off in a specific sequence—check your owner’s manual.
- Monitor after reset: After clearing the light, drive the truck normally and watch for the light to return—this helps confirm if the problem is fixed.
- Seek professional help when needed: If the light keeps coming back, it’s a sign of an ongoing issue that requires diagnostic expertise.
How to Disconnect Engine Light 1996 Ford Ranger
If you’re driving a 1996 Ford Ranger and that pesky check engine light keeps glowing on your dashboard, you’re not alone. Many owners of this classic compact truck face this issue at some point. While it’s tempting to just “make it go away,” it’s important to understand that the engine light—officially called the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)—is your truck’s way of saying, “Hey, something needs attention.”
In this guide, you’ll learn how to disconnect the engine light on a 1996 Ford Ranger safely and effectively. We’ll cover multiple methods, from simple battery resets to using diagnostic tools, and explain when it’s best to leave it to the professionals. By the end, you’ll know not only how to turn off the light but also how to prevent it from coming back.
Why Is the Engine Light On?
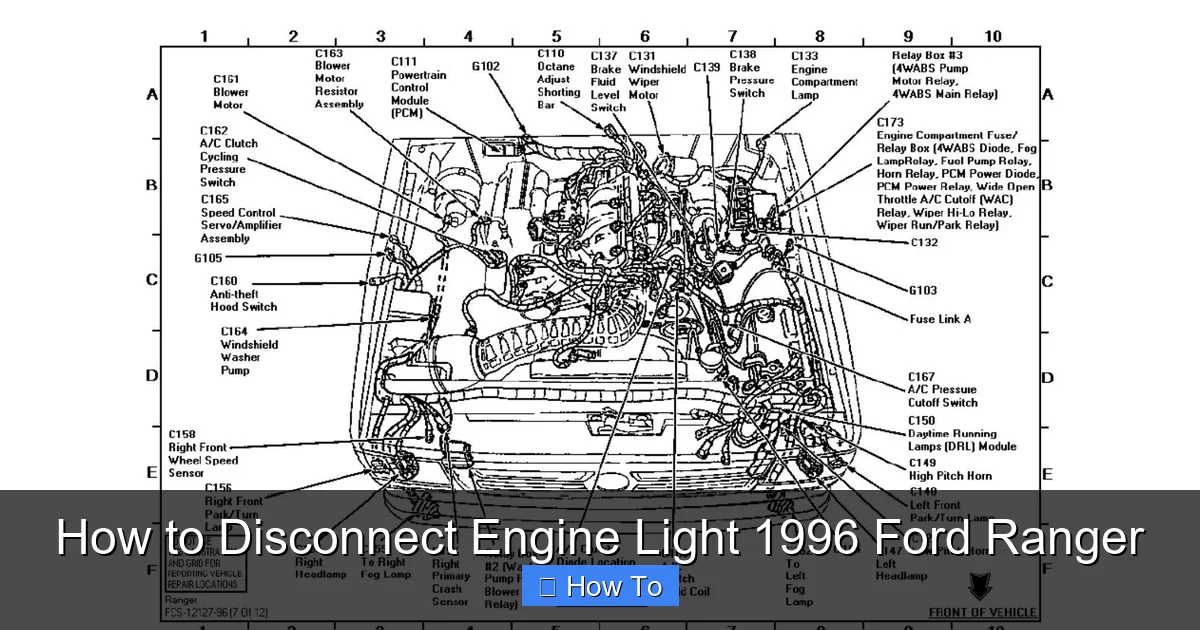
Visual guide about How to Disconnect Engine Light 1996 Ford Ranger
Image source: ww2.justanswer.com
Before you try to disconnect or reset the engine light, it’s crucial to understand why it’s on in the first place. The 1996 Ford Ranger uses an On-Board Diagnostics I (OBD-I) system, which monitors engine performance, emissions, and key sensors. When something goes outside normal parameters, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) triggers the check engine light.
Common causes include:
- A loose or faulty gas cap
- Oxygen sensor failure
- Mass airflow (MAF) sensor issues
- Spark plug or ignition coil problems
- Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve malfunction
- Catalytic converter inefficiency
Ignoring the light can lead to reduced fuel economy, poor performance, or even engine damage. So while “disconnecting” the light might seem like a quick fix, the real goal should be identifying and fixing the root cause.
Tools You’ll Need
Before starting, gather these tools:
- OBD-I scanner (compatible with Ford vehicles)
- Socket wrench set (usually 10mm for battery terminals)
- Safety gloves and glasses
- Owner’s manual (for PCM reset procedures)
- Flashlight (for better visibility under the dash)
If you don’t have an OBD-I scanner, you can purchase one online or borrow one from an auto parts store—many offer free code reading services.
Method 1: Use an OBD-I Scanner (Recommended)
The safest and most accurate way to disconnect the engine light is by using an OBD-I scanner. This tool reads the trouble codes stored in the PCM and allows you to clear them after repairs.
Step 1: Locate the Diagnostic Port
In the 1996 Ford Ranger, the OBD-I diagnostic port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It’s a 6-pin or 10-pin connector, often near the steering column. Look for a small, rectangular plug labeled “DLC” (Data Link Connector).
Step 2: Plug in the Scanner
Turn the ignition to the “ON” position (but don’t start the engine). Plug the OBD-I scanner into the DLC. The scanner should power up and display a menu.
Step 3: Read the Trouble Codes
Follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve the stored trouble codes. These codes (like P0300 for random misfire or P0440 for evaporative emissions leak) will tell you what’s causing the light.
Write down the codes and research them online or consult a repair manual. This step is critical—don’t skip it!
Step 4: Fix the Underlying Issue
Once you know the problem, address it. For example:
- If the code points to a loose gas cap, tighten or replace it.
- If it’s an oxygen sensor, consider replacing it (a common issue on older Rangers).
- If it’s a spark plug issue, inspect and replace as needed.
Step 5: Clear the Codes
After repairs, use the scanner to clear the trouble codes. This will reset the PCM and turn off the engine light. Turn the ignition off, wait 30 seconds, then restart the truck. The light should be off.
Step 6: Test Drive
Drive the truck for at least 10–15 minutes under normal conditions. This allows the PCM to run its self-tests. If the light stays off, the issue is likely resolved.
Method 2: Disconnect the Battery (Temporary Fix)
If you don’t have a scanner, disconnecting the battery can reset the PCM and turn off the engine light. However, this is a temporary solution and won’t fix the underlying problem.
Step 1: Turn Off the Engine
Make sure the truck is off and the keys are removed from the ignition.
Step 2: Locate the Battery
Open the hood and find the battery. The 1996 Ford Ranger typically has a 12-volt lead-acid battery on the driver’s side.
Step 3: Disconnect the Negative Terminal
Use a 10mm socket wrench to loosen the nut on the negative (-) battery terminal. Carefully remove the cable and tuck it away from the battery post so it doesn’t accidentally reconnect.
Step 4: Wait 10–15 Minutes
This allows the PCM to fully discharge and reset. Some sources recommend waiting up to 30 minutes for a complete reset.
Step 5: Reconnect the Battery
Reattach the negative cable and tighten the nut securely. Make sure it’s snug to avoid electrical issues.
Step 6: Start the Truck
Turn the ignition to “ON” and check if the engine light is off. Start the engine and let it idle for a few minutes.
Step 7: Monitor the Light
Drive the truck normally. If the light returns within a few days, the original problem still exists and needs repair.
Method 3: Manual PCM Reset (If Applicable)
Some 1996 Ford Rangers allow a manual PCM reset using the ignition key. This method varies by model and isn’t guaranteed, but it’s worth trying.
Step 1: Turn the Ignition to “ON”
Insert the key and turn it to the “ON” position (dashboard lights on, engine off).
Step 2: Turn It Back to “OFF”
Wait 5 seconds, then turn the key back to “OFF.”
Step 3: Repeat the Cycle
Repeat this on-off cycle three times within 10 seconds.
Step 4: Start the Engine
On the fourth turn, start the engine. The PCM may reset, and the engine light could turn off.
Check your owner’s manual to confirm if this procedure applies to your specific Ranger model.
What NOT to Do
While it might be tempting to physically disconnect the engine light bulb, this is strongly discouraged.
Never Remove or Disable the Light Bulb
Cutting wires or removing the bulb is dangerous and can:
- Cause electrical shorts
- Void your vehicle’s warranty (if applicable)
- Lead to inspection failures in states with emissions testing
- Mask serious problems that could damage your engine
The check engine light is a vital safety feature. Disabling it is not only unsafe but also illegal in many areas.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even after resetting the light, you might run into problems. Here’s how to handle them:
The Light Comes Back On Immediately
This usually means the issue wasn’t fixed. Recheck your repairs or use the scanner to read new codes.
The Light Flashes While Driving
A flashing light indicates a severe misfire that can damage the catalytic converter. Pull over safely and have the truck towed to a mechanic.
The Scanner Doesn’t Connect
Ensure the ignition is on, the scanner is OBD-I compatible, and the DLC port isn’t damaged. Try cleaning the connector with electrical contact cleaner.
Battery Reset Didn’t Work
The PCM may have non-volatile memory that retains codes. In this case, a scanner is your best bet.
When to See a Mechanic
If you’ve tried the above methods and the engine light keeps returning, it’s time to consult a professional. A certified mechanic can:
- Perform a full diagnostic scan
- Check for intermittent faults
- Inspect wiring and sensors
- Recommend long-term repairs
Ignoring persistent issues can lead to costly repairs down the road.
Conclusion
Disconnecting the engine light on a 1996 Ford Ranger isn’t about hiding a problem—it’s about understanding it and resolving it properly. While methods like battery disconnection or manual resets can turn off the light temporarily, the best approach is using an OBD-I scanner to diagnose and fix the root cause.
Remember: the engine light is your truck’s way of communicating. Listen to it. Fix the issue, reset the system, and enjoy a smoother, more reliable ride. With the right tools and knowledge, you can keep your Ranger running strong for years to come.
