This guide walks you through diagnosing and fixing check engine light code P0446, which relates to your vehicle’s EVAP system. You’ll learn how to inspect hoses, test the vent valve, and clear the code—no mechanic needed.
Key Takeaways
- Code P0446 means a problem with the EVAP system’s vent control circuit. This system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the air, and a fault can trigger the check engine light.
- The most common causes are a faulty vent valve, cracked hoses, or a loose gas cap. Start your diagnosis with these simple checks before moving to advanced testing.
- You can diagnose P0446 at home with basic tools. A multimeter, vacuum pump, and OBD2 scanner are all you need for most repairs.
- Always inspect the gas cap first—it’s the easiest and cheapest fix. A loose, damaged, or missing cap can cause this code on many vehicles.
- Replacing the EVAP vent solenoid is often the solution. Located near the fuel tank, this part controls airflow and fails over time due to dirt and moisture.
- Clear the code after repairs and test drive the vehicle. The light should stay off if the issue is truly resolved—don’t just reset it and hope.
- Ignoring P0446 can lead to failed emissions tests and reduced fuel efficiency. While not an emergency, it should be addressed promptly to maintain vehicle performance.
How to Fix Check Engine Light Code P0446
If your check engine light is on and you’ve scanned your vehicle to find trouble code P0446, don’t panic. This code is related to your car’s evaporative emission control system—commonly called the EVAP system. While it might sound complicated, fixing P0446 is often straightforward and can be done at home with basic tools.
In this guide, you’ll learn exactly what P0446 means, why it happens, and how to fix it step by step. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or just trying to save money on a mechanic, this guide will help you get your check engine light off and your car running cleanly again.
What Is Check Engine Light Code P0446?

Visual guide about How to Fix Check Engine Light Code P0446
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Code P0446 refers to a malfunction in the EVAP system’s vent control circuit. Specifically, it indicates that the engine control module (ECM) has detected an issue with the vent valve or its electrical circuit. The EVAP system is designed to capture fuel vapors from the gas tank and prevent them from escaping into the atmosphere. These vapors are stored in a charcoal canister and later burned in the engine during normal operation.
The vent valve—also known as the EVAP vent solenoid—is a key part of this system. It opens and closes to allow fresh air into the charcoal canister, helping to purge fuel vapors when needed. When the ECM detects that the vent valve isn’t responding correctly—either because it’s stuck, clogged, or receiving incorrect electrical signals—it triggers code P0446.
This code is considered a “non-emergency” fault, meaning your car will still run normally. However, it can cause you to fail an emissions test and may slightly reduce fuel efficiency over time. More importantly, it’s a sign that your vehicle isn’t operating as cleanly as it should.
Common Causes of P0446
Before diving into repairs, it’s helpful to understand what typically causes this code. Here are the most common culprits:
- Faulty EVAP vent solenoid: The most frequent cause. Over time, the solenoid can become clogged with dirt or fail electrically.
- Cracked or disconnected EVAP hoses: Rubber hoses in the EVAP system can dry out, crack, or come loose, causing leaks.
- Loose, damaged, or missing gas cap: A simple but often overlooked issue. Even a slightly loose cap can trigger P0446.
- Charcoal canister problems: A saturated or clogged canister can restrict airflow and cause venting issues.
- Wiring or connector issues: Corrosion, frayed wires, or loose connections to the vent solenoid can disrupt the signal.
- Failed ECM or sensor: Rare, but possible. Usually only suspected after all other components check out.
Knowing these causes helps you prioritize your troubleshooting. Start with the easiest fixes—like checking the gas cap—before moving on to more involved repairs.
Tools and Supplies You’ll Need
You don’t need a full garage to fix P0446. Here’s a list of tools and supplies that will make the job easier:
- OBD2 scanner (to read and clear codes)
- Multimeter (for testing electrical circuits)
- Handheld vacuum pump (optional, for testing solenoid function)
- Flashlight or work light
- Screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead)
- Pliers and needle-nose pliers
- Replacement gas cap (if needed)
- Replacement EVAP vent solenoid (if needed)
- New EVAP hoses (if cracked or damaged)
- Electrical contact cleaner
- Safety gloves and glasses
Most of these items are inexpensive and widely available at auto parts stores or online. If you’re planning to do more car maintenance in the future, investing in a good OBD2 scanner and multimeter is worth it.
Step 1: Check the Gas Cap
Before you do anything else, check your gas cap. It’s the simplest and most common fix for P0446—and it’s free if you already have a good one.
How to Inspect the Gas Cap
Start by removing the gas cap from your fuel filler neck. Look for signs of damage, such as cracks, warping, or a missing seal. The rubber gasket inside the cap should be intact and flexible—not brittle or torn.
Next, check if the cap clicks when you tighten it. Most modern gas caps are designed to click several times when properly sealed. If it doesn’t click, or if it feels loose, it may not be sealing correctly.
Test the Seal
You can do a quick test by reinstalling the cap and driving your car for a few miles. Then, scan for codes again. If P0446 returns, the cap may still be faulty—even if it looks okay.
If you suspect the cap is the issue, replace it with an OEM (original equipment manufacturer) or high-quality aftermarket cap. Avoid cheap universal caps, as they often don’t seal properly.
Pro Tip
Some vehicles have a “check fuel cap” message on the dashboard. If you see this, it’s a strong hint that the gas cap is the culprit. Even if you don’t see the message, always check the cap first—it’s the #1 cause of EVAP-related codes.
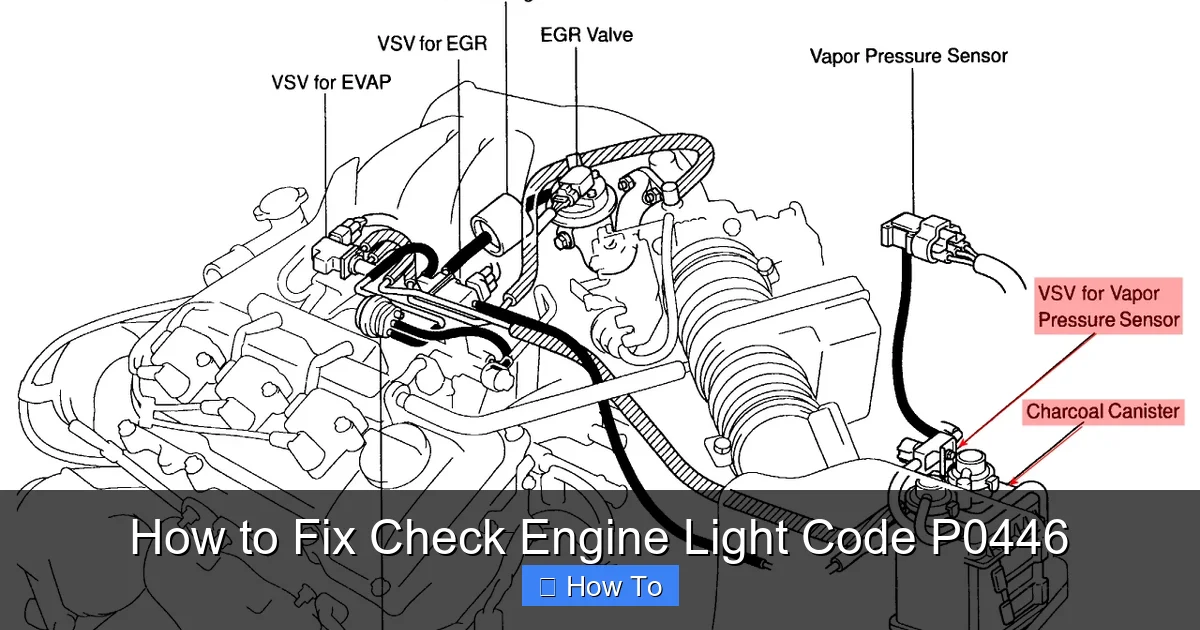
Step 2: Locate the EVAP Vent Solenoid
If the gas cap isn’t the problem, the next step is to find and inspect the EVAP vent solenoid. This part is usually located near the fuel tank, often mounted on or near the charcoal canister.
Finding the Solenoid
The exact location varies by make and model, but here are some common spots:
- Under the vehicle, near the rear passenger side wheel well
- Mounted on the charcoal canister (which is often near the fuel tank)
- Inside the fender liner (you may need to remove a plastic panel)
Consult your vehicle’s repair manual or search online for “EVAP vent solenoid location [your make and model]” to get precise instructions.
What to Look For
Once you locate the solenoid, inspect it visually. Look for:
- Cracked or broken housing
- Disconnected or damaged electrical connector
- Corrosion on the terminals
- Loose or cracked vacuum hoses connected to it
If you see any obvious damage, that’s likely your problem. If everything looks fine, you’ll need to test the solenoid electrically.
Step 3: Test the EVAP Vent Solenoid
The vent solenoid is an electrically controlled valve. When it receives power, it opens to allow air into the EVAP system. When power is removed, it should close. A faulty solenoid may be stuck open, stuck closed, or not responding to electrical signals.
Using a Multimeter to Test Resistance
Set your multimeter to measure resistance (ohms). Disconnect the electrical connector from the solenoid and touch the probes to the two terminals.
Most EVAP vent solenoids have a resistance between 20 and 50 ohms. Check your vehicle’s specifications, but if the reading is:
- Zero ohms: The solenoid is shorted (failed).
- Infinite ohms (OL): The solenoid is open (failed).
- Within range: The solenoid may still be functional—test further.
If the resistance is out of range, replace the solenoid.
Testing with a Vacuum Pump (Optional)
If you have a handheld vacuum pump, you can test the solenoid’s mechanical function. Connect the pump to the solenoid’s vacuum port and apply vacuum. The valve should hold vacuum when closed. If it leaks, the diaphragm inside may be torn.
You can also apply 12 volts to the solenoid (using a battery or power probe) and listen for a click. If you don’t hear a click, the solenoid may be stuck or electrically dead.
Pro Tip
Some solenoids are normally open or normally closed. Check your service manual to know which type your vehicle uses. Applying power should change the state—open to closed or vice versa.
Step 4: Inspect EVAP Hoses and Connections
Damaged or disconnected hoses are another common cause of P0446. The EVAP system relies on a network of small rubber hoses to move vapors and air. If any of these hoses are cracked, split, or loose, it can cause a leak that triggers the code.
How to Inspect the Hoses
Start at the charcoal canister and trace each hose to its connection point. Look for:
- Cracks or splits in the rubber
- Hoses that are brittle or hard
- Connections that are loose or disconnected
- Signs of fuel residue or dirt buildup
Pay special attention to hoses near heat sources (like the exhaust) or moving parts (like suspension components), as these areas are more prone to wear.
Testing for Leaks
You can do a simple smoke test if you have access to a smoke machine, but most DIYers don’t. Instead, try this:
- Use a spray bottle with soapy water.
- Spray around hose connections while the engine is running.
- If bubbles form, there’s a leak.
Alternatively, use an EVAP leak detector or take your car to a shop for a professional smoke test.
Replacing Damaged Hoses
If you find a damaged hose, replace it with the correct size and type. Use EVAP-rated hose, not regular vacuum hose, as it’s designed to resist fuel vapors. Cut the old hose carefully and install the new one with secure clamps.
Step 5: Check Wiring and Electrical Connections
Even if the solenoid tests okay, a wiring issue could still cause P0446. The ECM sends a signal to the vent solenoid, and if that signal is interrupted, the code will appear.
Inspecting the Wiring Harness
Trace the wire from the solenoid back to the main harness. Look for:
- Frayed or broken wires
- Corrosion at the connector
- Pinched or melted insulation
- Loose or damaged pins in the connector
Use electrical contact cleaner to clean the connector terminals. Reconnect firmly and ensure the locking tab clicks into place.
Testing for Power and Ground
With the ignition on (engine off), use your multimeter to check for voltage at the solenoid connector. One wire should have battery voltage (around 12V), and the other should be grounded by the ECM when activated.
If there’s no voltage, check the fuse for the EVAP system (usually in the under-hood fuse box). If the fuse is good, the issue may be in the wiring or the ECM.
Pro Tip
Use a wiring diagram for your specific vehicle to identify which wire is power and which is ground. This will help you test accurately.
Step 6: Replace the EVAP Vent Solenoid
If testing confirms the solenoid is faulty, it’s time to replace it. This is a common repair and usually takes less than an hour.
Steps to Replace the Solenoid
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal for safety.
- Locate the vent solenoid (as described earlier).
- Disconnect the electrical connector.
- Remove any mounting bolts or clips holding the solenoid in place.
- Disconnect the vacuum hoses (label them if needed to avoid confusion).
- Install the new solenoid in reverse order.
- Reconnect hoses, electrical connector, and battery.
Choosing a Replacement Part
Buy an OEM or high-quality aftermarket solenoid. Cheap parts may fail quickly. Check reviews and choose a reputable brand like ACDelco, Dorman, or OEM equivalent.
After Installation
Once the new solenoid is installed, clear the trouble code using your OBD2 scanner. Start the engine and let it idle for a few minutes. Then, take the car for a test drive of at least 10–15 miles to allow the ECM to run its EVAP monitor.
Step 7: Clear the Code and Test Drive
After making repairs, it’s essential to clear the code and verify the fix.
How to Clear the Code
Use your OBD2 scanner to erase the trouble code. Most scanners have a “clear codes” or “reset” button. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Monitor the Check Engine Light
After clearing the code, drive your car under normal conditions. The ECM will run a series of self-tests, including the EVAP monitor. This can take anywhere from a few miles to several days, depending on your driving habits.
If the check engine light stays off and no new codes appear, the repair was successful. If P0446 returns, double-check your work or consider a deeper issue like a faulty charcoal canister or ECM problem.
Pro Tip
Some vehicles require a specific drive cycle to complete the EVAP monitor. Check your repair manual for details. Common steps include:
- Start with a cold engine
- Drive at varying speeds (30–60 mph)
- Include stop-and-go traffic
- Let the car idle for a few minutes
Troubleshooting Tips and Common Mistakes
Even with careful work, you might run into issues. Here are some tips to avoid common pitfalls:
- Don’t ignore the gas cap: It’s the #1 cause of P0446. Always check it first.
- Don’t assume the solenoid is bad: Test it before replacing. A wiring issue could mimic a solenoid failure.
- Use the right hose: Regular vacuum hose degrades in the EVAP system. Use fuel-resistant hose.
- Label hoses during removal: It’s easy to mix them up. Take a photo before disconnecting.
- Don’t clear the code too soon: Let the system run its tests. Clearing too early may not reset the monitor.
- Check for technical service bulletins (TSBs): Some vehicles have known issues with P0446. Search online for your make and model.
When to See a Mechanic
While most P0446 issues can be fixed at home, there are times when professional help is needed:
- You’ve replaced the solenoid and hoses, but the code keeps returning.
- You suspect a problem with the charcoal canister or ECM.
- You don’t have the tools or confidence to test electrical circuits.
- Your vehicle requires a smoke test or advanced diagnostics.
A qualified mechanic can perform a full EVAP system test and pinpoint hard-to-find leaks or electrical faults.
Conclusion
Fixing check engine light code P0446 doesn’t have to be intimidating. By following this step-by-step guide, you can diagnose and repair the issue yourself—saving time and money. Start with the gas cap, inspect hoses and wiring, test the vent solenoid, and replace faulty parts as needed.
Remember, the EVAP system is crucial for reducing emissions and keeping your car running cleanly. Addressing P0446 promptly ensures your vehicle passes inspections and operates efficiently.
With the right tools and a little patience, you’ve got this. Clear that code, reset the light, and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with a job well done.