This guide walks you through how to reset the check engine light on a 2007 Chrysler Aspen using an OBD2 scanner or manual methods. You’ll also learn when it’s safe to reset the light and how to prevent future warnings.
Key Takeaways
- Use an OBD2 scanner for the safest reset: This tool reads and clears diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) without risking damage to your vehicle’s computer system.
- Never ignore the root cause: Resetting the light won’t fix the underlying issue—always diagnose the problem first to avoid repeat warnings.
- Manual reset methods may not work: Unlike older vehicles, the 2007 Chrysler Aspen typically requires a scanner; disconnecting the battery often fails to clear codes.
- Check common culprits first: Loose gas caps, faulty oxygen sensors, or spark plug issues are frequent triggers for the check engine light.
- Reset only after repairs: Clear the code only once the issue is resolved to ensure the light doesn’t return immediately.
- Keep records of repairs and codes: Documenting DTCs helps mechanics diagnose future problems faster and more accurately.
- Use quality parts for repairs: Cheap replacements can cause recurring issues and may not meet OEM standards for your Aspen.
How to Reset Check Engine Light on 2007 Chrysler Aspen
If you’ve noticed the dreaded check engine light glowing on your 2007 Chrysler Aspen’s dashboard, you’re not alone. This warning light can pop up for dozens of reasons—some minor, like a loose gas cap, and others more serious, like a failing catalytic converter. While it’s tempting to just make the light disappear, the real goal should be understanding why it came on in the first place.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn exactly how to reset the check engine light on a 2007 Chrysler Aspen—safely, effectively, and without causing further issues. We’ll cover everything from diagnosing the root cause to using an OBD2 scanner, manual reset attempts, and what to do if the light comes back. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or just want to save a trip to the mechanic, this guide has you covered.
By the end, you’ll know not only how to clear the light but also how to keep it off for good.
Understanding the Check Engine Light
Visual guide about How to Reset Check Engine Light on 2007 Chrysler Aspen
Image source: images.opinautos.com
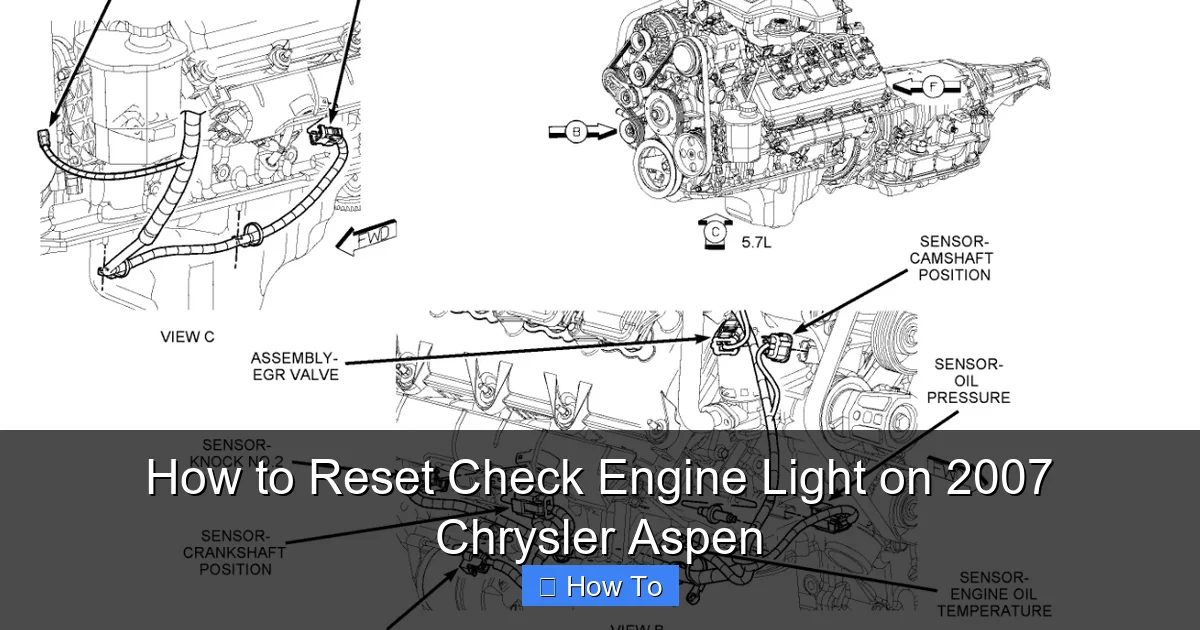
Before jumping into reset methods, it’s important to understand what the check engine light actually means. On your 2007 Chrysler Aspen, this light—officially known as the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)—is part of the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system (OBD2). When the engine control unit (ECU) detects a problem with emissions, fuel delivery, ignition, or other critical systems, it triggers the light and stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
These codes are standardized across all vehicles made after 1996, so a P0300 code, for example, always means a random/multiple cylinder misfire. The light can appear as either a steady glow or a flashing signal. A steady light usually indicates a less urgent issue, while a flashing light suggests a severe problem that could damage the catalytic converter if ignored.
Common Causes of the Check Engine Light in a 2007 Chrysler Aspen
The 2007 Chrysler Aspen, built on the Dodge Durango platform, shares many components with other Chrysler vehicles of the era. Common triggers for the check engine light include:
- Loose or damaged gas cap: This is the #1 cause of check engine lights. A loose cap allows fuel vapors to escape, triggering an evaporative emissions system (EVAP) code like P0455.
- Faulty oxygen (O2) sensors: These monitor exhaust gases and help the ECU adjust the air-fuel mixture. A failing O2 sensor can reduce fuel economy and increase emissions.
- Spark plug or ignition coil issues: Misfires are common in high-mileage Aspen models. Worn spark plugs or bad coils can cause rough idling and poor performance.
- Mass airflow (MAF) sensor problems: A dirty or malfunctioning MAF sensor can cause hesitation, stalling, and reduced power.
- Catalytic converter failure: Often a result of prolonged misfires, a clogged converter can trigger codes like P0420.
- Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve issues: A stuck EGR valve can cause knocking or pinging under acceleration.
- Evaporative emissions system leaks: Small leaks in hoses or the charcoal canister can set off EVAP codes.
Knowing these common causes helps you prioritize which systems to inspect before resetting the light.
Why You Should Diagnose Before Resetting
It’s crucial to understand that resetting the check engine light does not fix the problem—it only clears the warning. If you reset the light without addressing the underlying issue, it will likely come back within a few drive cycles. Worse, you might miss a serious problem that could lead to expensive repairs down the road.
For example, if your Aspen is misfiring due to a bad ignition coil, simply clearing the code won’t stop the misfire. The engine will continue to run poorly, potentially damaging the catalytic converter—a repair that can cost over $1,000.
That’s why the first step should always be diagnosis. Use an OBD2 scanner to read the trouble codes. Most auto parts stores (like AutoZone or O’Reilly) offer free code reading, or you can buy an affordable scanner for home use.
How to Read Trouble Codes
To read the codes yourself:
- Locate the OBD2 port under the dashboard, usually near the driver’s side knee panel.
- Plug in your OBD2 scanner and turn the ignition to the “ON” position (do not start the engine).
- Follow the scanner’s prompts to retrieve the codes.
- Write down the codes (e.g., P0171, P0303) and research their meaning online or in the scanner’s manual.
Once you know the code, you can determine the likely cause and decide whether to fix it yourself or take it to a mechanic.
Method 1: Resetting with an OBD2 Scanner (Recommended)
The most reliable and safest way to reset the check engine light on your 2007 Chrysler Aspen is by using an OBD2 scanner. This method ensures that the codes are properly cleared from the ECU’s memory and allows you to confirm the repair was successful.
What You’ll Need
- OBD2 scanner (Bluetooth or wired)
- Access to the OBD2 port (under the dashboard)
- Ignition key
Step-by-Step Instructions
Step 1: Ensure the Problem Is Fixed
Before resetting, make sure you’ve addressed the issue that triggered the light. For example, if the code was P0455 (large EVAP leak), tighten or replace the gas cap. If it was a misfire, replace the faulty spark plug or coil.
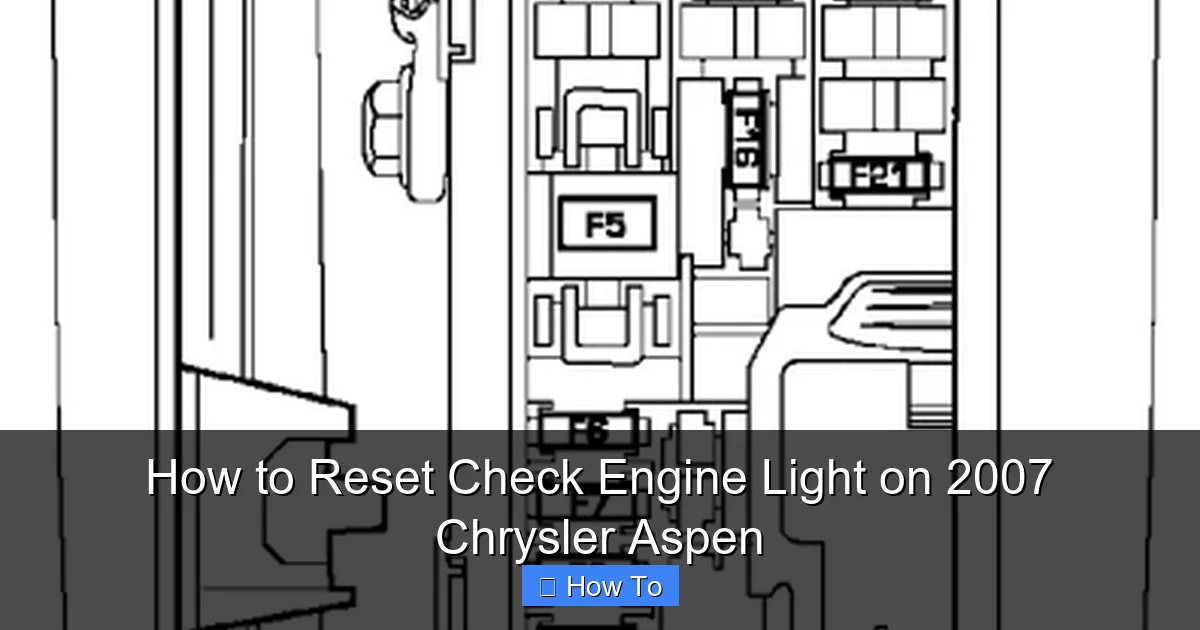
Step 2: Locate the OBD2 Port
In the 2007 Chrysler Aspen, the OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column. It’s a 16-pin connector, usually black or gray, and may be covered by a small panel.
Step 3: Plug in the Scanner
Insert the OBD2 scanner into the port. Make sure it’s fully seated. If you’re using a Bluetooth scanner, pair it with your smartphone or tablet using the companion app.
Step 4: Turn the Ignition On
Turn the key to the “ON” position (dashboard lights should illuminate), but do not start the engine. This powers up the ECU and allows the scanner to communicate with it.
Step 5: Read and Clear Codes
Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored trouble codes. Most scanners have a “Clear Codes” or “Erase DTCs” option. Select it to reset the check engine light.
Step 6: Verify the Reset
After clearing the codes, turn the ignition off and then back on. The check engine light should be off. If it returns immediately, the problem may not be fully resolved, or there could be a persistent issue.
Step 7: Take a Test Drive
Drive your Aspen for at least 10–15 minutes, including highway speeds, to allow the ECU to complete its drive cycle. This ensures all monitors are reset and the system checks for recurring problems.
Tips for Using an OBD2 Scanner
- Choose a scanner with live data and freeze frame features to better understand the conditions when the code was set.
- Some scanners can reset readiness monitors, which is helpful before an emissions test.
- If the light comes back, re-scan for new or pending codes—these can give clues about intermittent issues.
Method 2: Manual Reset (Battery Disconnection)
Some drivers try to reset the check engine light by disconnecting the battery. While this method works on older vehicles, it’s less effective on modern cars like the 2007 Chrysler Aspen due to advanced memory systems.
How It Works
Disconnecting the battery cuts power to the ECU, which can reset some systems. However, many trouble codes are stored in non-volatile memory and won’t be cleared this way. Additionally, disconnecting the battery can reset other systems, including:
- Radio presets
- Power window settings
- Climate control memory
- Adaptive transmission settings
Step-by-Step Battery Disconnection Method
Step 1: Turn Off the Engine and Remove the Key
Ensure the vehicle is off and the key is out of the ignition.
Step 2: Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal
Use a wrench to loosen the nut on the negative (black) battery terminal. Remove the cable and isolate it so it doesn’t touch the terminal.
Step 3: Wait 15–30 Minutes
Leave the battery disconnected for at least 15 minutes. Some recommend up to 30 minutes to ensure the ECU fully resets.
Step 4: Reconnect the Battery
Reattach the negative cable and tighten the nut securely.
Step 5: Start the Vehicle
Turn the ignition on and check if the check engine light is off. If it remains off after a short drive, the reset may have worked.
Limitations of This Method
- Many OBD2 codes are not cleared by battery disconnection.
- The light may return after the ECU relearns driving patterns.
- You may need to relearn idle settings or reprogram the radio.
For these reasons, the OBD2 scanner method is strongly preferred.
Method 3: Drive Cycle Reset (Natural Clearing)
In some cases, the check engine light will turn off on its own after the problem is fixed and the vehicle completes a specific drive cycle. This is known as a “natural” or “automatic” reset.
What Is a Drive Cycle?
A drive cycle is a series of driving conditions that allow the ECU to test various emissions and engine systems. Once all monitors pass, the check engine light may turn off.
Typical Drive Cycle for 2007 Chrysler Aspen
While exact cycles vary, a common sequence includes:
- Start the engine and let it idle for 2–3 minutes (cold start).
- Drive at 30–40 mph for 3–5 minutes.
- Accelerate to 55–60 mph and maintain speed for 5–10 minutes.
- Decelerate without braking (coast) for 1–2 minutes.
- Repeat the cycle 2–3 times over several days.
When This Method Works
This approach is most effective for minor issues like a loose gas cap that’s been tightened. If the problem was temporary and the system passes all tests, the light may go off.
However, if the issue persists, the light will return. This method should not be relied upon for serious problems.
Troubleshooting: What If the Light Comes Back?
If you’ve reset the check engine light but it returns after a few days or weeks, don’t panic—this is common. Here’s how to troubleshoot:
Re-Scan for Codes
Use your OBD2 scanner to check for new or pending codes. Sometimes, the original code returns, or a new one appears, indicating a related issue.
Check for Intermittent Problems
Some issues, like a failing oxygen sensor or loose wiring, only occur under certain conditions (e.g., cold weather, high load). Keep a log of when the light appears and what you were doing (accelerating, idling, etc.).
Inspect Common Wear Items
On a 2007 Aspen with high mileage, consider inspecting:
- Spark plugs and wires (replace every 60,000–100,000 miles)
- Ignition coils (test with a multimeter or swap method)
- O2 sensors (front and rear)
- Air filter and MAF sensor (clean with MAF cleaner)
- Fuel cap and EVAP system hoses
Seek Professional Help
If you’ve tried multiple fixes and the light keeps returning, it’s time to visit a trusted mechanic. They can perform advanced diagnostics, such as smoke testing for EVAP leaks or checking fuel pressure.
Preventing Future Check Engine Light Issues
The best way to avoid resetting the check engine light is to prevent it from coming on in the first place. Here are some proactive tips:
Regular Maintenance
Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for your 2007 Chrysler Aspen. This includes:
- Oil changes every 3,000–5,000 miles
- Spark plug replacement at recommended intervals
- Air filter changes every 15,000–30,000 miles
- Fuel system cleaning every 30,000 miles
Use Quality Fuel and Parts
Fill up at reputable gas stations and use top-tier gasoline when possible. Cheap fuel can contain contaminants that foul sensors and injectors. When replacing parts, choose OEM or high-quality aftermarket components.
Check the Gas Cap Regularly
Make it a habit to ensure the gas cap is tight after every fill-up. A simple twist until it clicks can prevent EVAP codes.
Monitor Dashboard Warnings
Don’t ignore other lights, such as the oil pressure or temperature warning. These can indicate issues that may eventually trigger the check engine light.
Conclusion
Resetting the check engine light on your 2007 Chrysler Aspen doesn’t have to be a mystery. While it’s tempting to just make the light disappear, the real value comes from understanding and fixing the underlying problem. The safest and most effective method is using an OBD2 scanner to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes after repairs are completed.
Manual methods like battery disconnection are unreliable on modern vehicles, and natural resets only work for minor, temporary issues. Always prioritize diagnosis and repair over simply clearing the light.
By following the steps in this guide, you’ll not only reset the check engine light but also keep your Aspen running smoothly for years to come. Remember: a little prevention and timely maintenance go a long way in avoiding future warnings.