Diagnosing the engine light on a 1991 Cadillac DeVille can seem overwhelming, but with the right tools and knowledge, it’s manageable. This guide walks you through every step—from reading trouble codes to fixing common problems—so you can save time and money.
Key Takeaways
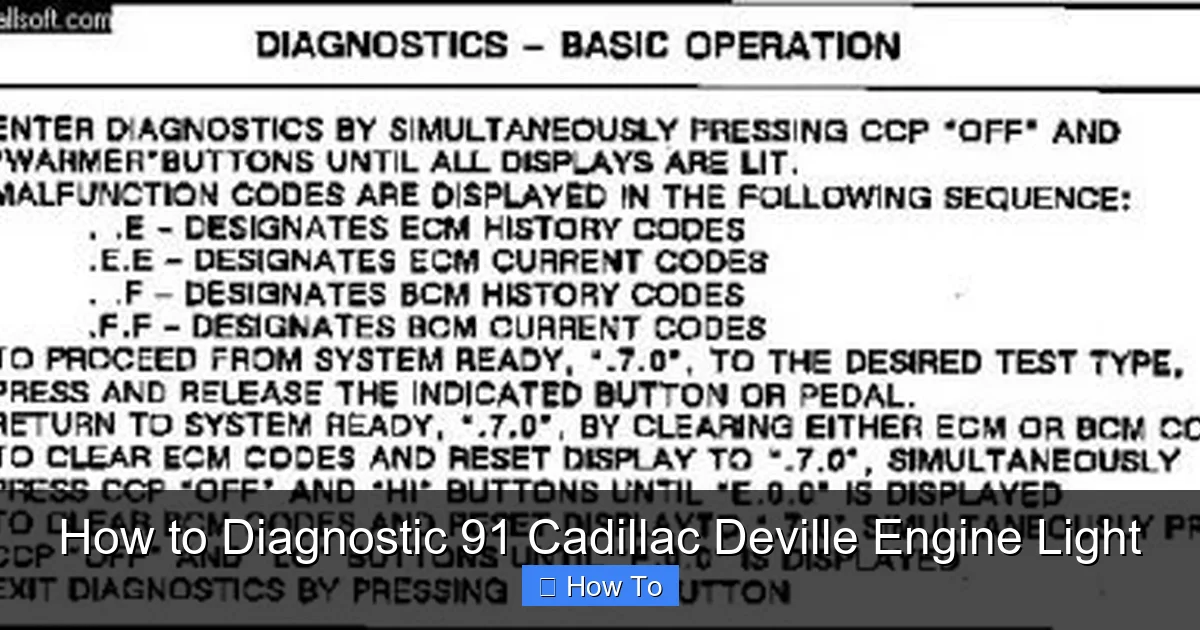
- Use an OBD-I scanner or paperclip method: The 1991 Cadillac DeVille uses OBD-I, so you’ll need a compatible scanner or a simple paperclip to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Locate the ALDL connector: The Assembly Line Diagnostic Link (ALDL) under the dashboard is where you’ll connect your tool to retrieve engine codes.
- Interpret flash codes correctly: If using the paperclip method, count the Check Engine Light flashes to identify specific trouble codes.
- Common issues include O2 sensor, EGR valve, and vacuum leaks: These are frequent culprits behind the engine light in older Cadillacs.
- Clear codes after repairs: Always reset the system by disconnecting the battery or using a scanner to confirm the fix worked.
- Regular maintenance prevents future warnings: Keep up with tune-ups, fluid checks, and sensor inspections to avoid repeat issues.
- Consult a repair manual for accuracy: Factory service manuals provide detailed diagrams and code definitions specific to your DeVille.
How to Diagnostic 91 Cadillac Deville Engine Light
If you own a 1991 Cadillac DeVille and the dreaded “Check Engine” light has popped on, don’t panic. While it might feel like a major problem, many causes are minor and fixable at home. This guide will walk you through how to diagnostic 91 Cadillac Deville engine light issues step by step—using simple tools, clear instructions, and practical tips. By the end, you’ll know how to read trouble codes, identify common problems, and take action to get your luxury sedan running smoothly again.
The 1991 DeVille uses an older On-Board Diagnostics system called OBD-I, which predates the standardized OBD-II systems found in cars from 1996 onward. This means you can’t just plug in any modern scanner. But don’t worry—there are still reliable ways to pull diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and figure out what’s going on under the hood.
What You’ll Need
Before we begin, gather these items:
- Paperclip or jumper wire (for manual code reading)
- OBD-I compatible scan tool (optional but helpful)
- Flashlight
- Notepad and pen
- Basic hand tools (screwdrivers, wrenches)
- Repair manual for 1991 Cadillac DeVille (recommended)
Having the right tools makes the process faster and more accurate. If you plan to work on your car regularly, investing in an OBD-I scanner designed for GM vehicles is worth it.
Step 1: Locate the ALDL Connector
The first step in how to diagnostic 91 Cadillac Deville engine light is finding the diagnostic port. On your 1991 DeVille, this is called the Assembly Line Diagnostic Link (ALDL) connector.
Where to Find It
The ALDL connector is usually located under the driver’s side dashboard, near the steering column. It’s a rectangular plastic plug with 12 pins arranged in two rows of six. It may be tucked behind a panel or covered by a small flap—use your flashlight to spot it.
Visual guide about How to Diagnostic 91 Cadillac Deville Engine Light
Image source: 2carpros.com
Why It Matters
This port allows the car’s computer (ECM) to communicate with external tools. It’s your gateway to reading trouble codes that trigger the engine light.
Step 2: Choose Your Diagnostic Method
There are two main ways to read codes on a 1991 DeVille: using a scan tool or the manual paperclip method. Both work, but the paperclip method is free and doesn’t require special equipment.
Method A: Using an OBD-I Scan Tool
If you have an OBD-I scanner compatible with GM vehicles (like the Tech 1 or a modern equivalent), simply plug it into the ALDL connector. Turn the ignition to “ON” (don’t start the engine), and the scanner will display any stored trouble codes. Write them down for reference.
Method B: The Paperclip Method (Manual Code Reading)
This is the most common DIY approach. Here’s how it works:
- Turn the ignition off.
- Straighten a paperclip and insert one end into pin A and the other into pin B of the ALDL connector. (Pin A is usually the top-left pin; pin B is top-right—check your manual to confirm.)
- Turn the ignition to “ON” (engine off).
- Watch the Check Engine Light on the dashboard. It will begin to flash in a pattern that corresponds to trouble codes.
For example, if the light flashes once, pauses, then flashes nine times, that’s code 19. Each code is displayed as a series of short and long flashes.
Step 3: Interpret the Trouble Codes
Once you’ve retrieved the codes, it’s time to figure out what they mean. The 1991 DeVille uses a standard GM OBD-I code set, but some codes are specific to Cadillac models.
Common Codes and What They Mean
- Code 12: No RPM signal—often indicates a problem with the ignition system or crankshaft sensor.
- Code 13: Oxygen (O2) sensor circuit malfunction—common in older cars due to sensor wear.
- Code 14: Coolant temperature sensor (ECT) low input—could mean a faulty sensor or wiring issue.
- Code 15: Coolant temperature sensor high input—sensor may be shorted or disconnected.
- Code 32: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system fault—very common in DeVilles; often caused by a clogged EGR valve.
- Code 33: Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor high input—could indicate a vacuum leak or faulty sensor.
- Code 44: Lean exhaust indication—usually points to a vacuum leak or failing O2 sensor.
Always cross-reference your codes with a reliable source, such as a factory service manual or trusted online database. Some codes may have multiple causes, so don’t jump to conclusions.
Step 4: Inspect and Test Suspected Components
Now that you know the code, it’s time to investigate. Let’s look at a few common issues and how to test them.
Oxygen (O2) Sensor
The O2 sensor monitors exhaust gases and helps the engine adjust the air-fuel mixture. A faulty sensor can trigger codes 13 or 44.
- Locate the sensor—usually on the exhaust manifold or downpipe.
- Check for corrosion, damage, or loose wiring.
- Use a multimeter to test resistance (refer to your manual for specs).
- If faulty, replace it. O2 sensors typically last 60,000–100,000 miles.
EGR Valve
The EGR valve reduces emissions by recirculating exhaust gas. Over time, it can get clogged with carbon, causing code 32.
- Find the EGR valve—usually mounted on the intake manifold.
- Remove it and inspect for carbon buildup.
- Clean it with carburetor cleaner or replace it if damaged.
- Check the vacuum lines connected to the valve—replace if cracked or brittle.
Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks are sneaky and often cause lean codes (like 44). They occur when air enters the engine unmetered.
- Listen for a hissing sound under the hood.
- Spray carb cleaner around hoses and gaskets—if the engine RPM changes, you’ve found a leak.
- Inspect all vacuum lines, especially those near the intake manifold and brake booster.
- Replace any cracked or disconnected hoses.
Step 5: Clear the Codes and Test Drive
After making repairs, you need to clear the trouble codes to see if the engine light stays off.
How to Clear the Codes
- Disconnect the negative battery cable for 10–15 minutes. This resets the ECM.
- Reconnect the battery and turn the ignition to “ON” (don’t start the engine).
- Wait a few seconds—the Check Engine Light should remain off.
- Start the car and take it for a short test drive.
If the light stays off, congratulations—you’ve successfully fixed the issue! If it returns, the problem may be more complex or intermittent.
Troubleshooting Tips
Even with the right steps, diagnosing the engine light can be tricky. Here are some tips to avoid common pitfalls:
- Don’t ignore intermittent codes: Some problems only appear under certain conditions (e.g., cold starts or high speeds). Keep a log of when the light comes on.
- Check the basics first: A loose gas cap can sometimes trigger the light. Make sure it’s tight and the seal is intact.
- Use quality parts: Cheap sensors or valves may fail quickly. Stick with reputable brands like AC Delco for GM vehicles.
- Watch for multiple codes: One issue can trigger several codes. Focus on the root cause, not just the symptoms.
- When in doubt, consult a mechanic: If you’re stuck or the problem involves internal engine components, professional help may be needed.
Preventing Future Engine Light Issues
The best way to avoid repeat visits from the Check Engine Light is regular maintenance.
- Replace spark plugs and wires every 30,000–50,000 miles.
- Change the air filter and fuel filter as recommended.
- Inspect vacuum lines annually for cracks or leaks.
- Use high-quality fuel and consider fuel system cleaners periodically.
- Keep the EGR valve and throttle body clean.
A well-maintained 1991 Cadillac DeVille can still run reliably for many more years. The engine light is just your car’s way of saying, “Hey, check this out!”—and now you know how to listen.
Conclusion
Learning how to diagnostic 91 Cadillac Deville engine light doesn’t require a mechanic’s degree—just patience, the right tools, and a methodical approach. Whether you use a paperclip or a scanner, reading trouble codes is the first step toward fixing the problem. From O2 sensors to EGR valves and vacuum leaks, most issues are manageable with basic tools and know-how.
Remember, the engine light is a warning, not a death sentence. With this guide, you’re equipped to tackle it head-on, save money on diagnostics, and keep your classic Cadillac running strong. Stay proactive with maintenance, and your DeVille will reward you with smooth, reliable performance for years to come.